Vaccine inequality: A new beginning or another missed opportunity?

Recently, UN Secretary-General Antonio Guterres sharply criticized the “wildly uneven and unfair” distribution of COVID-19 vaccines. Addressing the Security Council, Guterres noted that just 10 countries have administered 75 percent of all vaccinations. Meanwhile, 130 countries had not received a single dose.
In two reports – The Tragedy of Missed Opportunities (April 2020) and The Tragedy of More Missed Opportunities (August 2020) – I documented four missed opportunities in the mobilization against the global pandemic last year.
Without vaccination equity, the ongoing year could represent the fifth missed opportunity and even more challenging long-term prospects.
Failure of early mobilization
The first opportunity emerged around the first recorded case (Dec 30, 2019), and the WHO’s announcement of the international emergency (Jan 30, 2020). Then, the epicenter of the outbreak was still in Wuhan, Hubei.
After mid-January, China introduced social distancing and launched a historical quarantine, which soon began to flatten the curve. Mobilization was also initiated in China’s Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, Singapore and other regions.
The Trump White House was informed about the virus on January 3, 2020, and the European CDC began its risk assessments only days later. But neither resulted in a phased mobilization.
United States had the institutions to battle the virus, but the Trump administration chose not to use them, presumably to “protect the economy and the markets”.
In Europe, many countries were willing to fight the virus, but lacked the common institutions needed for effective regional containment.
Ineffective and late mobilization
The second critical opportunity to contain the virus covers the first quarter of 2020. On March 10, the WHO declared it a pandemic. Although the epicenter had already moved to Europe and then to the US, full mobilization in both ensued only weeks after the pandemic warning - almost three months later than mobilization in proactive Asian locations.
Worse, until early February, most WHO members failed to provide WHO full country reports, which hurt international cooperation at a critical moment.
While complacency and inadequate preparedness contributed to shortages and challenges, sensational media coverage was high on hype, but short on facts. That caused an “infodemic” contributing in the West to anti-Chinese and anti-Asian hate crimes (which still prevail).
Even worse, many international observers began an odd battle against the WHO, its chief Tedros Ghebreyesus and China in which effective containment was paving the way to the rebounding of the economy.
Failed mobilization
In cumulative terms, the period of the third missed opportunity covers the first half of 2020. It could be dated from the WHO’s pandemic declaration, yet broader responses in the US and Europe only began around late March and early April.
As escalation continued in Europe, the COVID-19 epicenter moved from the West Coast to the East Coast in the US while quarantines and lockdowns diffused worldwide.
It was only now that the social distancing measures first initiated in China in January were more fully introduced in the West, but with widespread enforcement failures.
As late mobilization proved less effective, the epidemic curve was not flattened, but fattened; in many countries for weeks, in some for months. As a result, soaring cases began to foster increasing numbers of new mutations.
In countries where quarantines and restrictions were initially shunned, particularly the UK and Sweden, the number of cases and deaths soared alarmingly.
Furthermore, outbreaks spread to poorer economies, particularly across South America, India and the rest of South and Southeast Asia, with weaker healthcare systems. Though the diffusion of the pandemic started in the first quarter, the quarantine escalation followed in the second quarter.
Meanwhile, massive economic damage spread rapidly around the world.
Unwarranted and resource failures
In the course of the fourth missed opportunity, the outbreak epicenter stayed in or returned to the major advanced economies, particularly the United States and the Americas, several countries in Europe, and Japan.
In the US, the Trump administration’s politicized and grossly ineffective mobilization resulted in new waves already in the summer. In Europe, institutional failures led to such waves in the fall.
Many failures were unwarranted in the sense that public health policies based on science and international multilateral cooperation could have avoided much of the damage.
Although many poor countries tried to fight the outbreak, most lacked adequate resources. In due time, these public health failures in the developing economies are likely to have adverse feedback effects elsewhere.
More importantly, due to limited testing and inadequate data, a great number of cases and deaths continue to go undetected in many economies, particularly in the poorer ones. As a result, official estimates downplay the true pandemic damage.
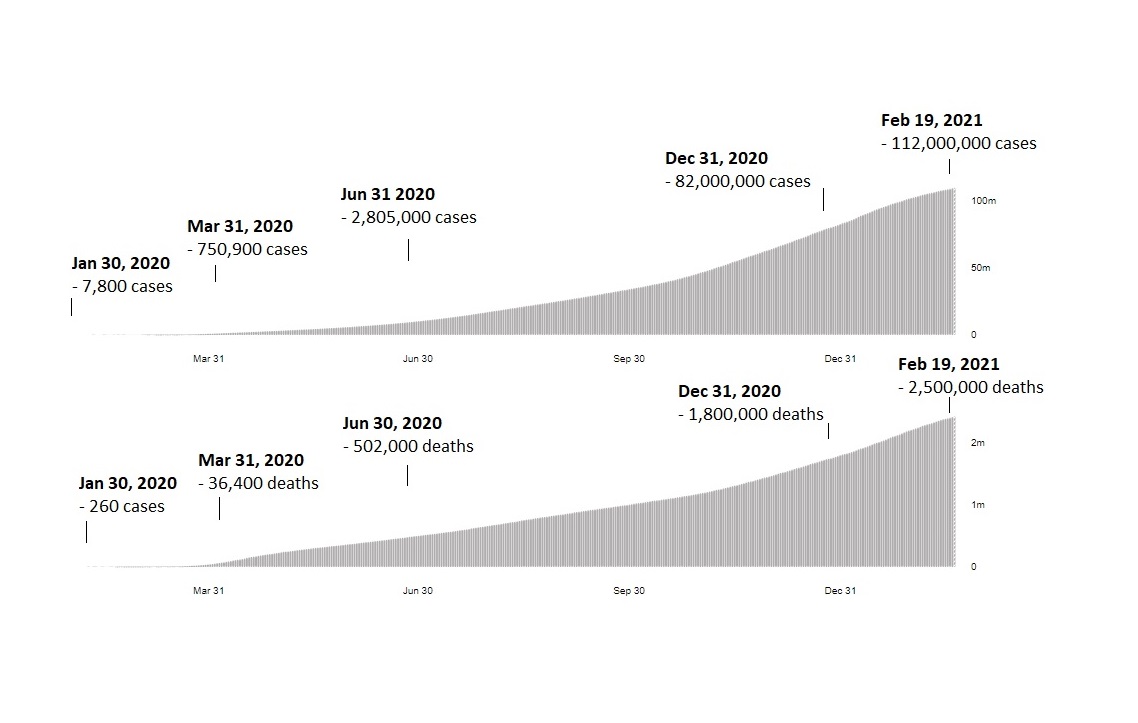
Thanks to these four major failures, the human costs of the pandemic have soared from 7,800 cases over a year ago to some 112 million; and deaths from about 260 to 2.5 million (see Figure). Of course, the number of real cases – as opposed to confirmed ones – is likely to be significantly higher.
Figure Human Costs of Four Missed Opportunities
Cumulative Confirmed Cases and Deaths
Vaccine inequality: Toward the fifth missed opportunity?
By early February, two months into the global rollout of coronavirus vaccines, 150 million doses of vaccines had been administered in fewer than 70 countries.
Early vaccine administration has favored only a few nations, which have hoarded 80 percent of the doses used so far. In contrast, 130 countries with 2.5 billion people have not administered a single dose.
The countries that have been favored the most in the early vaccine rollout have been mainly high-income economies, especially the G7 countries. The Biden administration is doing what it can to reverse the Trump administration’s policy mistakes, but more than a year has been missed.
Due to the gross failure of multilateral cooperation, the number of COVID-19 cases and deaths is now far, far higher than initially anticipated. At the same time, the huge spread of the global pandemic has ensured a rapidly-rising number of mutations.
In recent months, new variants of the original virus, which may be more contagious and damaging, have been found in the UK, Brazil, South Africa, and the US. Worse, a recombination of the variants detected in the UK and California may have caused a wave of cases in Los Angeles.
With more than 112 million infected people verifiably creating antibodies against the virus, still other versions are likely to emerge that could evade the immune system, reinfect even recovered persons and become more widespread.
The longer the crisis lingers, the greater remains the probability for potentially malignant outcomes – and, by the same token, for new pandemic waves, new restrictions and lockdowns, more economic damage, lost years, even lost decades.
Only decisive multilateral action across political differences – including WHO’s containment plan and UN’s global vaccination plan - can try to overcome still another failure of multilateralism that’s looming ahead.
It’s time to do the math: These plans could cost a few billion dollars, whereas pandemic relief spending, according to Bank of America, amounted to $20 trillion already last August.
What on earth are we waiting for?
Dr. Dan Steinbock is an internationally recognized strategist of the multipolar world and the founder of Difference Group. He has served at the India, China and America Institute (USA), Shanghai Institutes for International Studies (China) and the EU Center (Singapore).
The opinions expressed here are those of the writer and do not necessarily represent the views of China Daily and China Daily website.
































