Green hydrogen, ammonia, ethanol highlighted for nation's carbon reduction


Expanding the use of green hydrogen, ammonia and ethanol will be crucial for China to achieve deep cuts in carbon emissions while ensuring domestic energy security, as the future growth of power generation will mainly come from nonfossil resources, according to political advisers and industry experts.
China, being the world's largest producer and consumer of hydrogen and ammonia, holds significant strategic importance in fostering the development of sustainable green hydrogen, ethanol and ammonia, said Jiang Yi, chairman of China Huadian Corp Ltd, who is also a member of the 14th National Committee of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference.
Jiang suggested comprehensive research on policy support, market mechanisms and standard systems for the hydrogen, ethanol and ammonia sectors to drive commercial-scale development and application of "new energy+hydrogen/ethanol/ammonia-based energy".
The process of producing hydrogen, ethanol and ammonia from renewable energy resources and using them as a carrier for energy storage, which can later be converted back to electricity, is considered a pivotal option for deep decarbonization at the terminal end. They have been gaining more international attention for their potential as an emissions-free fuel.
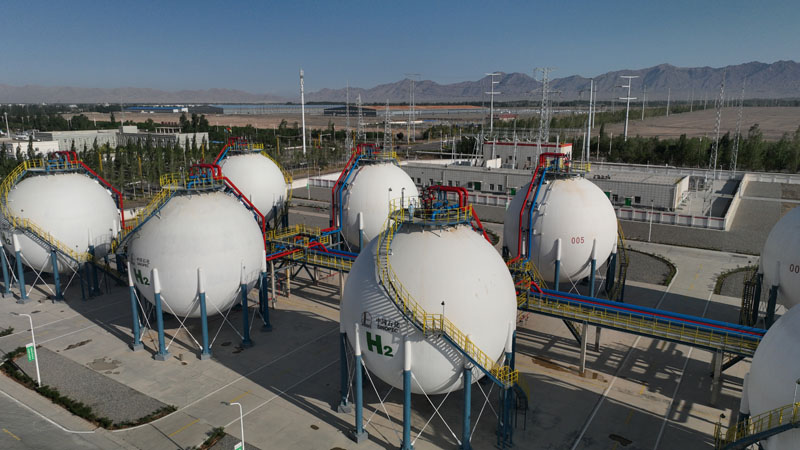
Currently, hydrogen is mainly produced from carbon dioxide and natural gas without using carbon capture, utilization and storage technology. It therefore generates massive carbon emissions during the process, known as "gray hydrogen".
"Blue hydrogen" has its carbon emissions captured and stored, or reused.
Just like hydrogen, there are several different types of ammonia, depending on the energy used for its production. Green ammonia — produced using wind, solar or hydropower — is becoming the most preferable form of the fuel as it is carbon-free.
China's national emissions trading scheme (ETS) currently covers only power generation enterprises. Sectors such as chemicals and steel, which are strongly associated with the widespread application of green hydrogen, ethanol and ammonia, have not been included.
Experts believe that green hydrogen, ethanol and ammonia could be a key to the success of the country's carbon peak and neutrality goals, which aim to peak carbon emissions by 2030 and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060.
With clear demand and the potential for use in various industries, green hydrogen, ethanol and ammonia are gaining increasing attention from governments and companies looking to shift away from fossil fuels to renewable alternatives, said Luo Zuoxian, head of intelligence and research at the Sinopec Economics and Development Research Institute.
Seeing the potential for green hydrogen, ethanol and ammonia, governments across the world are exploring a variety of renewable sources to decarbonize their transport sectors and other areas. Luo believes green hydrogen, ammonia and ethanol have been emerging as a clean and versatile fuel with the potential to revolutionize various sectors.
On the other hand, China's green hydrogen production costs are declining as a result of increased technological breakthroughs, while greater investment that supports innovations in technologies can help further reduce production costs, said Luo.
As China is currently the world's largest hydrogen producer and consumer, it has substantial room for further development, he said.
Wu Mouyuan, vice-president of the China National Petroleum Corp Economics and Technology Research Institute, said hydrogen's ability to produce energy without emitting CO2 makes it a promising solution for decarbonizing sectors that are challenging to directly electrify, such as heavy industry, aviation and long-haul overland transport.
By serving as a clean fuel alternative, hydrogen can replace traditional fossil fuels while playing a crucial role in consuming and storing renewable energy, making it an indispensable energy alternative for achieving deep emissions reductions at the terminal stage, Wu said.
Jiang said Huadian aims to step up new energy project construction this year, including solar and offshore wind power, amid the country's green energy transition.
It eyes establishing an integrated energy industry supply chain that covers hydrogen, energy storage and carbon trade, while accelerating technological research and innovation to further integrate digital technologies and artificial intelligence with energy production, so as to foster new and high-quality productive forces, he said.