Flights of kites
An ancient folk craft tradition floats across time and still soars to new heights, Cheng Yuezhu reports.

Editor's note: Traditional arts and crafts are supreme samples of Chinese cultural heritage. China Daily is running this series to show how master artisans are using dedication and innovation to inject new life into the heritage. In this installment, we explore how traditional kite-makers give flight to their creativity today.
Many people hold at least one memory of a kite from their childhoods — be it a simple yet classic diamond or a colorful bird-shaped kind with vividly flapping wings.
It could be a sunny spring day in a pastoral landscape with family members. As the wind picks up, the flyer runs as fast as they can, until the kite ascends high into the sky and dances in the air.
The kite that Yang Hongwei, 58, from Yangjiabu village in Shandong province's Weifang, remembers, however, is slightly different. It was a gigantic dragon-headed centipede that stretched for 360 meters and took dozens of people to fly.
That was at the third Weifang International Kite Festival in 1986. To celebrate their village's legacy of crafting kites, her grandfather, Yang Tongke, and uncle, Yang Qimin — both master kite-makers — boldly envisioned and created a model 10 times bigger than any they'd ever made.
Weifang is renowned as the "world capital of kites", and Yangjiabu village has long remained at the heart of local production.

Yang Hongwei, who was born to a family of artisan kite-makers in the village, became a national-level representative inheritor of Weifang kite-making techniques this year.
"Here in Weifang, we have a saying, 'there's nothing you can think of that can't fly'. We have the ideal wind conditions, and so many kite lovers, top-notch artisans and different kinds of handmade kites," she says.
Yangjiabu is small enough to qualify as a village, yet is home to two national-level intangible cultural heritage items — kites and Yangjiabu New Year pictures, a type of traditional woodblock printing used to decorate people's homes during Spring Festival.
Both art forms emerged in Yangjiabu in the Ming Dynasty (1368-1644) and prospered in the Qing Dynasty (1644-1911).
"Our kites' decorations draw inspiration from the New Year pictures, so each one carries its own story and auspicious connotations," Yang Hongwei says.
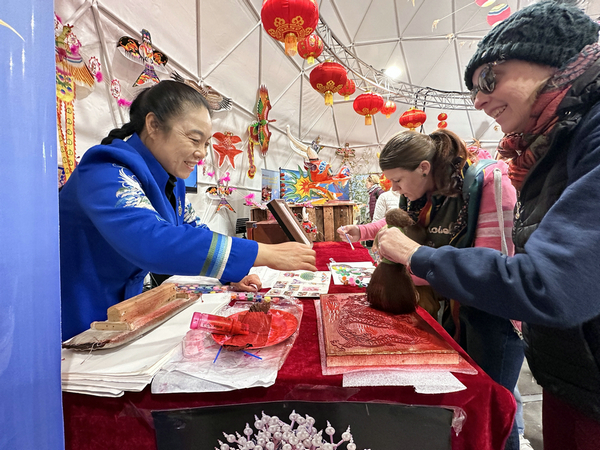

She brought a variety of representative Weifang kites to the recent 37th International Kite Festival in Berck-sur-Mer, France, including a dragon-headed centipede kite with images of 100 children, which are often depicted as the subjects of local New Year pictures.
The kite features a dragon head with a body and tail fashioned from around 50 discs, each of which is hand-painted with images of children, carrying wishes for longevity, wealth, prosperity and other blessings.
"Throughout history, kites have been close to people's daily lives and influenced by folk traditions," says Ma Zhiyao, a professor at Tianjin University who specializes in folklore and intangible cultural heritage.
"They have not only become embedded in folk culture but also provided entertainment and physical activity. This heritage has been passed down, demonstrating the enduring vitality of Chinese civilization."
Kites' origins can be traced back to the late Spring and Autumn Period (770-476 BC), with historical accounts attributing their invention to the philosopher Mozi, who spent three years crafting a wooden hawk, which is considered a prototype for today's kites.
Later, master carpenter and engineer Lu Ban made improvements by substituting wood with bamboo.
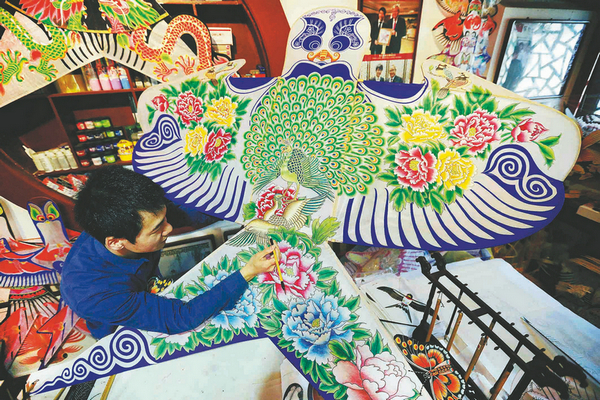

Kites are considered one of the earliest forms of aircraft. Ancient books recorded their functions in aerial reconnaissance and transmitting military intelligence.
During the Eastern Han Dynasty (25-220), inventor Cai Lun improved papermaking techniques, leading to the invention of "paper hawks", which resembled kites as we know them today.
"Kites' origins reveal the remarkable ability and creativity of ancient Chinese to imitate nature and explore its mysteries," Ma says.
"They observed birds and thought of using wood and paper to make objects that could soar in the sky. They were driven by curiosity and a spirit of scientific exploration to understand and harness the power of wind."
During the Tang Dynasty (618-907), the relative stability and prosperity made paper more affordable, and kites truly became part of people's lives.
As kite-making techniques became more refined, varieties adorned with imagery and that produced sound effects were developed.

This period gradually also saw kite flying becoming a custom during festivals. Late Tang-era poet Luo Yin wrote a poem about kite flying on the Cold Food Festival, which then fell directly before the springtime Tomb Sweeping Day and was later merged with it.
The custom was popularized in the Song Dynasty (960-1279). By the Ming and Qing dynasties, significant progress was continuing in design, style, production, decoration and flying skills.
"Many literati liked to make silk kites as gifts for their families and friends. They'd carefully select refined materials and then paint the silk cover by hand. These kites were exquisite and lasting," Ma says.