Artificial diamonds shine in Henan
Dazzling lab stones more preferred for industrial use due to cost-effectiveness


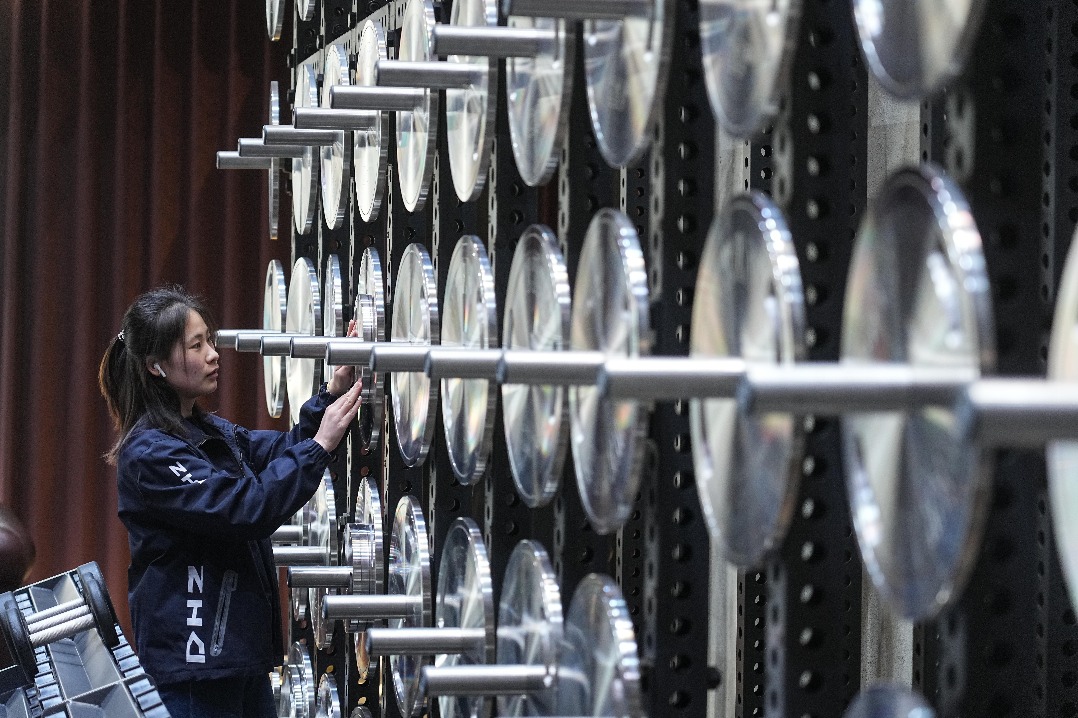
SF Diamond has established a lab-grown diamond factory in Henan province that has an annual production capacity of about 700,000 carats, making it the largest chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process-based diamond producer in the country.
Experts said this is a significant breakthrough in Henan's ultra-hard materials industry and will further facilitate the development of emerging sectors like electric vehicles, following self-developed microwave plasma CVD (MPCVD) equipment that has overcome foreign technology blockades.
"CVD technology is a proven method for producing large, high-quality industrial diamonds. The commissioning of this 700,000-carat (production capacity) project addresses a shortfall in our industry," said Fang Haijiang, chairman of SF Diamond.
Sun Zhaoda, secretary-general of the Superhard Material (Industrial Diamond) Association of China (IDAC), said, "The establishment and commissioning of this factory will further promote MPCVD equipment manufacturing, as well as the diamond production and processing industry chain in the province."
In the 1960s, China's first lab-grown diamond was successfully developed in Zhengzhou, capital of Henan. After six decades of development, Henan has become a major producer of ultra-hard materials.
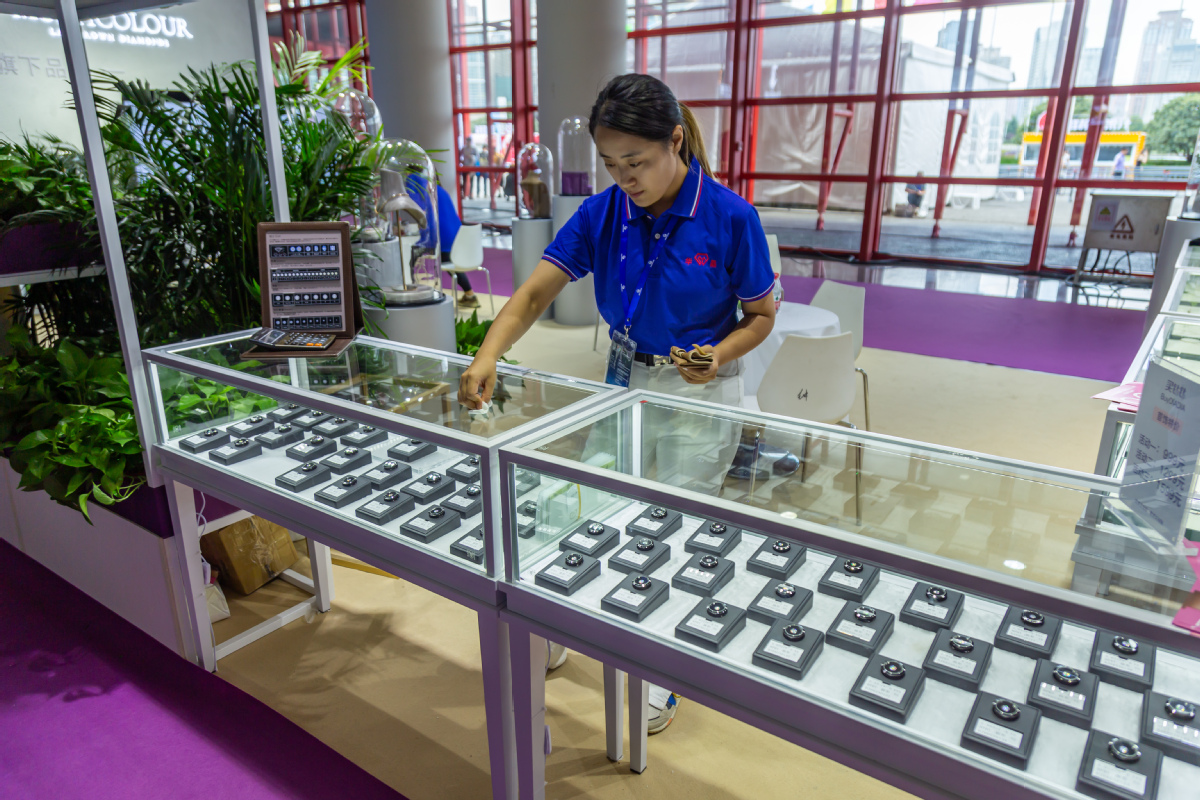
According to the IDAC, China's lab-grown diamond output accounts for about 95 percent of the global total, with Henan contributing about 80 percent of the national output.
As the hardest natural material, diamonds boast high chemical inertness, high thermal conductivity, low friction coefficient, ultrawide bandgap and high optical transparency. These properties make diamonds essential in various advanced manufacturing fields.
However, natural diamonds are nonrenewable, expensive to mine, limited in supply and have uncontrollable impurities, making them unsuitable for widespread industrial use.
Consequently, lab-grown diamonds that have identical physical and chemical properties to natural diamonds are preferred for industrial applications as they are more cost-effective and easier to access. Experts said lab-grown diamonds are becoming critical in fields like quantum computing, quantum communication and quantum precision measurement.
Compared with the high-pressure high-temperature (HPHT) method, which is more common in Chinese factories for growing diamonds, CVD, a method being adopted by an increasing number of companies, is considered less expensive and quicker to produce diamonds.
Li Hongli, deputy general manager of SF Diamond's subsidiary for manufacturing CVD diamonds, said it takes about a month and a half for a 5-carat diamond to grow in the new factory.
SF Diamond said that among various CVD methods, MPCVD is currently among the most popular for producing electronic-grade diamonds. In electronics, these diamonds are used for heat sinks, high-frequency devices and laser diodes.
MPCVD is also considered an optimal process for diamond semiconductor materials for applications in high-power electronics that require precise control and efficiency, like those in electric vehicles, the company said.
In 2022, the US limited exports of technologies that support the production of advanced semiconductors. These include gallium oxide and diamond-based substrates of ultrawide bandgap semiconductors.
This made self-developed MPCVD essential for China's ultra-hard materials sector and emerging industries, SF Diamond said.
In recent years, SF Diamond has increased investments in research and development of MPCVD technology, and completed the development and verification of MPCVD equipment.
The company's efforts have echoed calls by the Henan provincial government to develop ultra-hard materials epitomized by lab-grown diamonds.
Qi Xin in Zhengzhou contributed to this story.