Scientists provide evidence for existence of ancient ocean on Mars

BEIJING -- Chinese researchers have cooperated with their overseas counterparts to identify subsurface dipping reflectors indicative of an ancient prograding shoreline on Mars, according to a recent research article published in journal PNAS.
The findings offer the most direct subsurface evidence of an ancient ocean on the red planet.
Although orbital images have identified ancient shorelines that suggest the northern lowlands of Mars may once have been covered by an ancient ocean spanning a third of the Martian surface, the hypothesis of an ancient Martian ocean remained controversial.
The controversy is due to the inconsistent elevation distribution of the ancient shorelines inferred from remote sensing data, as well as the impacts, weathering, and resurfacing processes that Mars has experienced over the past 4 billion years, which may have distorted or obscured evidence of the ancient ocean's surface.
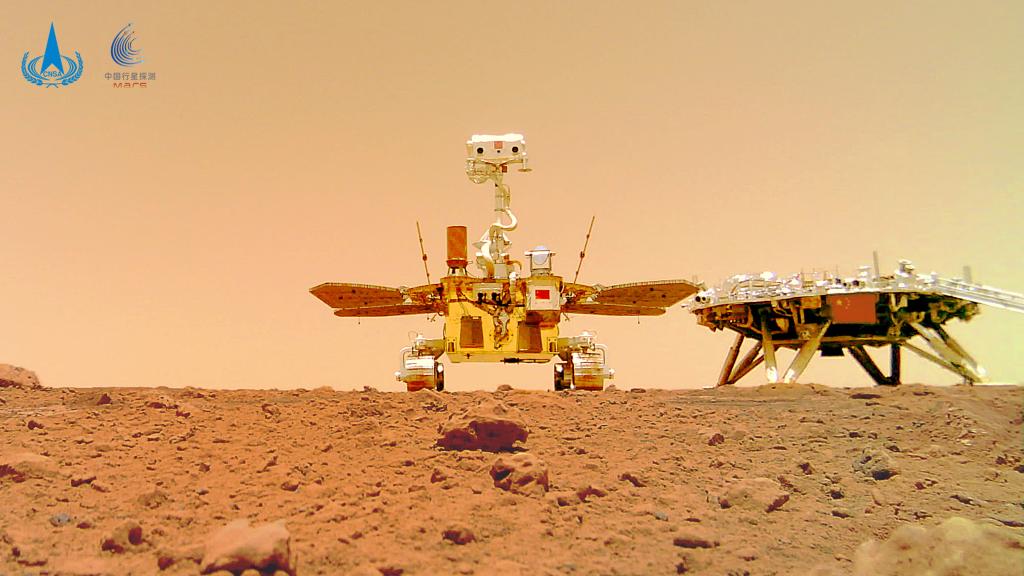
China's Mars rover Zhurong successfully landed in southern Utopia Planitia on Mars in May 2021. It had traveled 1,921 meters by May 2022 on the red planet, collecting abundant scientific data.
Zhurong is equipped with a dual-frequency subsurface-penetrating radar system, which is capable of probing subsurface structures and potential water ice deposits.
Through radar data gathered by the rover, the researchers from Guangzhou University, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Tongji University, University of California, Berkeley, and Pennsylvania State University, identified extensive dipping deposits in the subsurface of southern Utopia Planitia.
The reflectors dipped unidirectionally with inclinations in the range from six to 20 degrees and were imaged to a thickness of 10 to 35 meters along an uninterrupted 1.3 kilometers northward shoreline-perpendicular traverse.
These structures were similar to the radar imaging results of coastal sediments on Earth. Their consistency and physical properties ruled out other origins such as aeolian sand dunes or fluvial alluviation.
The structure, thickness, and length of the section supported voluminous supply of onshore sediments into a large body of water, rather than a merely localized and short-lived melt event, the article noted.
Such findings support the existence of an ancient Martian ocean in the northern plains and provide crucial insights into the evolution of the ancient Martian environment.
- American musician: the Silk Road influenced American music
- China upgrades Ragasa to super typhoon
- Over 5,000 photographers showcase work in Shanxi's ancient city of Pingyao
- Li calls on US lawmakers to enhance exchanges, ties
- Luxury brands drop ads featuring S. Korean actress after she insults China
- Jiangmen activates Chikungunya fever L3 emergency response