Chinese scientists develop wearable repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation device

BEIJING -- A group of Chinese researchers has developed a wearable repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) device, according to a recent research article published in the journal Nature Communications.
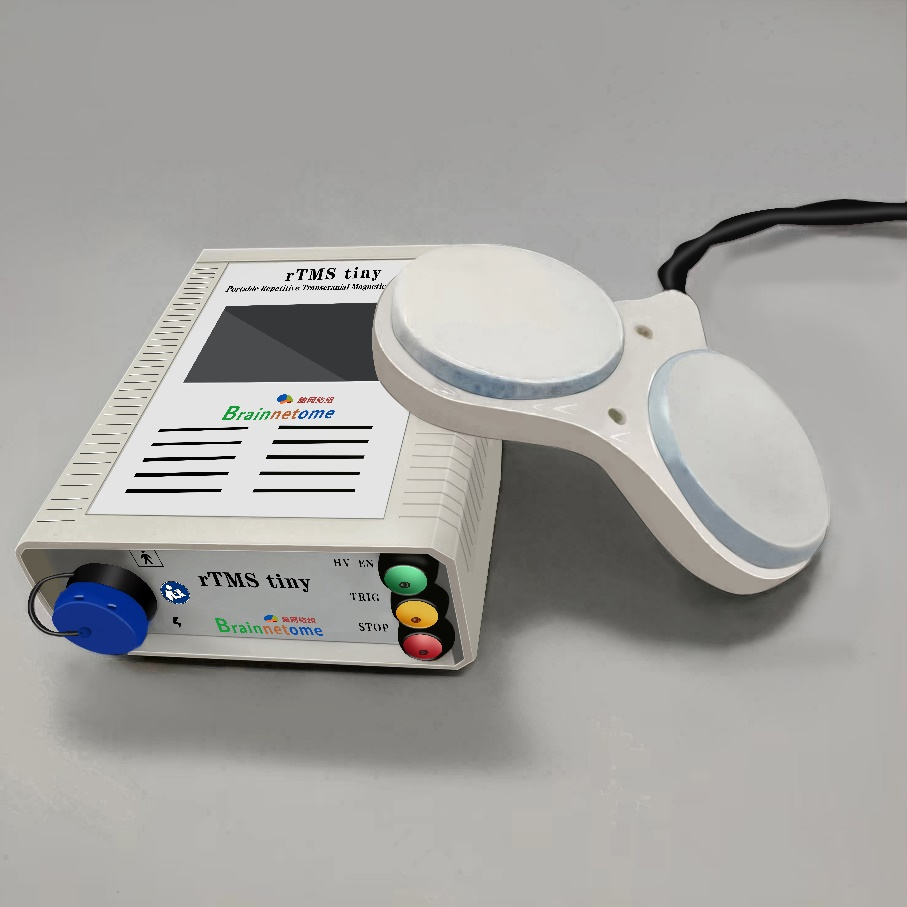
The rTMS device is widely used to treat various neuropsychiatric disorders and to explore the brain, but its considerable power consumption and large size limit its potential for broader utility, such as applications in free behaviors or in home and community settings.
Researchers from the Institute of Automation, under the Chinese Academy of Sciences, developed the battery-powered wearable rTMS device through lightweight magnetic core coil designs, high-power-density and high-voltage pulse driving techniques. The combined weight of the stimulator and coil is only three kilograms.
It uses only 10 percent of the power consumption compared with commercial rTMS devices even though the stimulus intensity and repetition frequency are comparable, the research article noted.
The researchers demonstrated the effectiveness of this device during free walking, showing that neural activity associated with the legs can enhance the cortex excitability associated with the arms. This advancement allows for high-frequency rTMS modulation during free behaviors and enables convenient home and community rTMS treatments.
Wearable rTMS devices have the potential to be integrated with non-invasive brain signal detection technologies in the future, said Liu Hao, senior engineer at the Institute of Automation. By real-time decoding of brain signals to optimize the rTMS regulation process, a wearable closed-loop rTMS neuromodulation system can be formed.
This will make it possible for closed-loop brain-computer interfaces to move from laboratory settings to large-scale real applications, said Liu.
- Four missing after SW China mudslide
- Guizhou achieves remarkable success in advancing high-quality development, official says
- Global influencers explore Yantai's wine culture
- China records sustained drop in environmental disputes
- Visitors impressed after boarding CNS Shandong on 'open day'
- Intl forum on ecology opens with over 1,000 domestic and foreign guests