Authorities hot on trail of missing cultural relics
 |
|
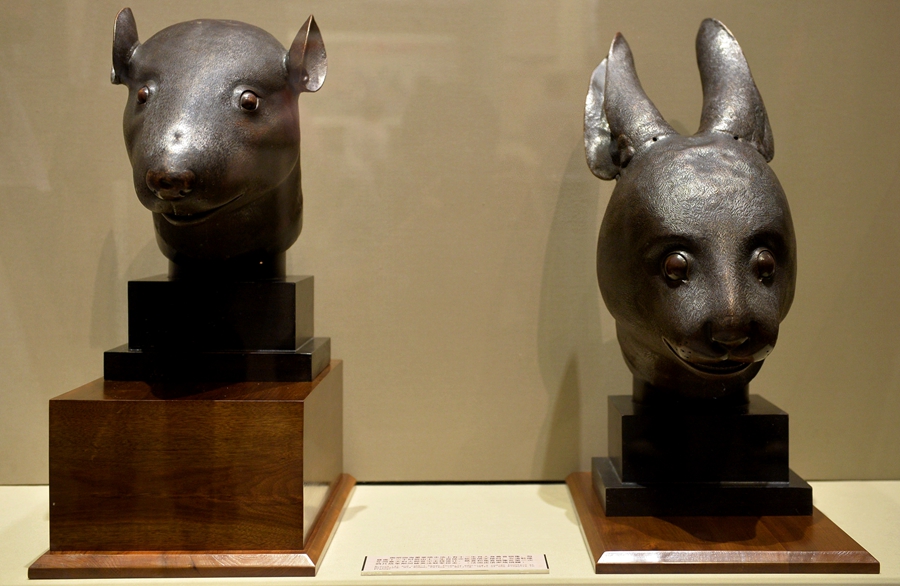
Bronze rabbit and rat head statues. [Photo/Xinhua] |
A study by UNESCO shows there are at least 1.64 million sets of Chinese cultural relics scattered across 200 museums in other countries and regions. The China Cultural Relics Academy, an academic organization, estimates the number would be 10 million if private collections were counted.
Many such treasures were looted during wars and other unrest in China from the late 19th century to the early 20th century. Large-scale theft occurred in the 1990s because of the boom in international market demand.
In 2013, French businessman Francois-Henri Pinault donated the bronze heads of a rabbit and a rat to China. They had been robbed by British and French forces from the Old Summer Palace in Beijing during the Second Opium War (1856-1860).
In 2014, China drafted an international rule on the return of cultural property-China's first such effort. The Dunhuang Recommendation has led to more success in China's efforts since then.
In July 2015, 32 gold ornaments made of gold foil from the Spring and Autumn Period (770-476 BC) were returned to Gansu province. They had been illegally excavated there in the 1990s. French collectors Francois Pinault, Francois-Henri Pinault's father, and Christian Deydier obtained the ornaments and donated them to the Guimet Museum in Paris. But the donation was halted and the ornaments were returned to China.
In February, Hsing Yun, the abbot of Fo Guang Shan Buddhist temple in Taiwan, returned a stolen Buddha head to the mainland. The artifact was taken from Youju Temple in Hebei province in 1996. It was donated to Fo Guang Shan by a Taiwan businessman.
The abbot, then 89, escorted the 1,500-year-old Buddha head, and it is now displayed at the Hebei Museum. China's mainland has been the victim of many relic thefts in the last century, the abbot said at the time.
Diplomatic channels often must be tapped to recover long-lost items, Huo said. The Convention on the Means of Prohibiting and Preventing the Illicit Import, Export and Transfer of Ownership of Cultural Property, a major international law, mainly covers post-1970 violations.
Consequently, China has signed bilateral agreements with some 20 countries, including the United States, Italy and Switzerland, to fight the smuggling of stolen relics as a supplement for the convention.
Last year, when a 1,000-year-old statue containing a mummified monk was displayed in Budapest, on loan from a Dutch collector, it aroused suspicion. Chinese authorities found the artifact had been stolen from Yangchun village in Fujian province in 1995.
But diplomatic negotiations have yet to secure its return. Nevertheless, the villagers have initiated a lawsuit for repatriation, and the legal process is ongoing in a Dutch court. The collector will appear in court for the first time this month, China News Service said.
"We looked for the missing statue for 20 years," said Lin Wenqing, a villager who is leading the repatriation lawsuit. "The statue is a part of our families."
While some Chinese collectors are willing to pay good money to bring lost relics home, Song Xinchao, deputy director of the State Administration of Cultural Heritage, does not encourage such so-called "patriotic actions".
"These relics were taken abroad through illegal means," he told China Daily previously. "But purchasing them will, in a way, confirm the legitimacy of such thefts, and make the prices of these items even higher in the international market."
He said diplomatic and legal approaches should be used more often.
Nevertheless, on some occasions, the country has had to pay to bring treasures back home when there is a threat they could fall into others' hands, or even disappear. In 2002, the administration entrusted other institutions to negotiate with a collector to buy Yanshan Ming, an 11th-century calligraphy masterpiece, from abroad for 29.99 million yuan ($4.4 million) and the work is now housed at the Palace Museum in Beijing.
"No one knows how much more we would need to pay if we bought it now," said Shan Jixiang, then head of administration and now director of the museum.