Global COVID-19 responses: 'Zero COVID-19 Case Policy' vs. 'Coexisting with COVID-19 Policy'

4. Is there a trade-off between protecting economy and protecting people's lives?
In the responding policies taken by countries around the world to contain the pandemic, the focal point is how to strike a balance between public health and the economic impact. Through rigorous lockdown measures, China successfully contained COVID-19. China is currently trying hard to maintain the "zero COVID-19 case" situation. China's COVID-19 response can be called the "Zero COVID-19 Case Policy".
On the contrary, most Western countries reopened economy when there were still infections, although they had placed various restrictions on people's activities, such as imposing lockdowns or declaring a state of emergency. The measures taken by those countries can be called the "Coexisting with COVID-19 Policy".
The second part of the article will compare the "Zero COVID-19 Case Policy" and the "Coexisting with COVID-19 Policy" and verify an efficient route to fight against the disease.
(1) China: Prioritizing COVID-19 response
In the aftermath of 2002-2003 SARS, the Chinese government formulated the Regulation on the Urgent Handling of Public Health Emergencies, the National Response Plan for Public Emergencies, and the National Response Plan for Public Health Emergencies, on the basis of the Law of the People's Republic of China on Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Diseases. In 2007, the Emergency Response Law of the People's Republic of China was announced, further systemizing the above-mentioned law, regulation and response plans. On Jan. 20, before Wuhan was put into a lockdown, China's National Health Commission released a statement to classify the novel coronavirus pneumonia as a category B infectious disease under the law on prevention and control of infectious diseases but take preventive and control measures of category A infectious diseases, meaning that the fight against COVID-19 had been launched.
It is exactly because the law, regulation and response plans mentioned above were put into place after the SARS epidemic that China could swiftly impose lockdowns, activate the top-level public health emergency response and take other mandatory measures to curb the novel coronavirus. With a priority placed on epidemic response, mitigation measures would not be altered willfully, regardless of the economic impact. In fact, despite cries for the resumption of production and schools as soon as possible across China, the Chinese government stuck to the requirements for reopening, such as only when there were no new cases.
According to Chart 3, China has done whatever it took in economic terms to prevent the spread of COVID-19, and then resumed normal economic activities soon. Seen in the longer span of time, lockdowns and level II public health emergency response were like strong medicine, but a good therapy to keep the situation under control. It is difficult to keep new case numbers at zero. Therefore, once a new infection case was spotted, China would implement strict restrictions and large-scale COVID-19 testing in the area to prevent the spread of the virus.
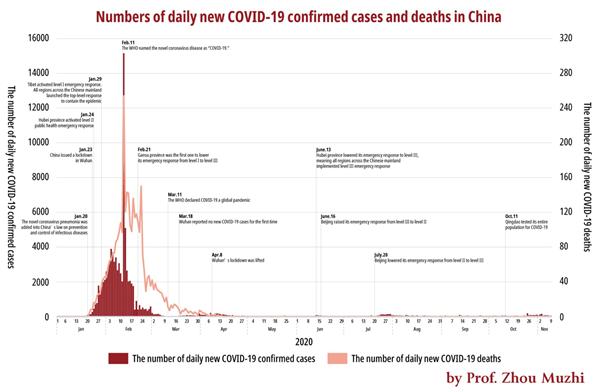
Note: The number of infection cases in China marked in the chart does not include numbers of asymptomatic cases and imported cases.
Source: China's National Health Commission
(2)Report 9and Western countries' responses
On March 16, 53 days after Wuhan's lockdown, British epidemiologist Neil Ferguson and other scientists published "Report 9: Impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) to reduce COVID-19 mortality and healthcare demand". The report predicted that the novel coronavirus would infect eight out of 10 people, with 510,000 deaths in the U.K. over the next four months, if measures were not in place. Even with mitigation measures, such as isolating infected people, home quarantining, and restricting senior people to their homes, there would be still 250,000 deaths in the country. With strict lockdown rules, the death toll could be limited to 20,000[14]. Ferguson told the Science and Technology Committee that the move to balance economy and COVID-19 response while tolerating the spread of the virus to some extent was wrong, noting that lockdown was the only option. On March 23, one week after the report was published, the British government announced a nationwide lockdown, prohibiting residents from going out if not necessary and closing schools and most businesses.
The report projected at most 2.2 million deaths in the US In the light of the report, US President Trump extended the federal social distancing guidelines, which originally expired on March 30, to April 30[ 15].
British journal Nature published a report titled "The effect of large-scale anti-contagion policies on the COVID-19 pandemic" on June 8. The report analyzed the effect of policies rolled out by six countries—China, South Korea, Italy, Iran, France and the US The report estimated that in more than three months from January to April 6, those six countries protected hundreds of millions of people from getting infected, through (1) travel restrictions, (2) social distancing through the cancellations of events and suspensions of educational, commercial and religious activities, (3) quarantines and lockdowns, and (4) additional policies such as emergency declarations[16].
Despite obvious effect, lockdown measures have met a lot of resistance among many people who thought they limited human activities and wrought damage on social and economic activities. Many countries began to lift lockdowns prematurely, after the spread of COVID-19 slowed.
(3) "Zero COVID-19 Case Policy" vs. "Coexisting with COVID-19 Policy"
Wuhan's lockdown was lifted after it met very rigorous requirements. It was only after Wuhan had reported no new cases for the past 16 days that the lockdown was lifted. I think that is the radical "Zero COVID-19 Case Policy".
The Chinese government issued risk-grading criteria on Feb. 17, classifying counties, cities and districts that report no cases or no new cases in the past 14 days as low-risk areas[17].
After successfully containing the first outbreak, China still went all out to maintain the "zero case" situation across the country. Once a new case was confirmed, strict restrictions and large-scale testing would be implemented immediately to block the spread of COVID-19. For example, after three asymptomatic cases were confirmed in Qingdao of Shandong province on Oct. 11, the city tested its entire population and traced people moving out of the city. By Oct. 16, more than 11 million people had been tested.
Contrary to China, European countries and the US lifted lockdown restrictions very soon, because they were eager to reduce the impact of COVID-19 on their economy. A study by the Germany-based IFO Institute for Economic Research and the Helmholtz Centre for Infection Research was released on May 13[18].The study said keeping the Rt (the effective reproduction number, refering to the average number of people who become infected by an infectious person) at 0.75 provides the safest balance between hammering out output and risking a new outburst of infections. In other words, keeping the Rt at 0.75 can minimize the economic costs without jeopardizing the medical objectives. The study is an endorsement of the "Coexisting with COVID-19 Policy" in the academic circle. However, the report failed to come up with effective measures to keep the Rt at 0.75 in response to the highly contagious virus. Therefore, the golden balance put forward in the report is just a hallow theory. The report provides theoretical backing to the "Coexisting with COVID-19 Policy" adopted by European countries and the US, which was the scourge of later resurgence in those countries.
In fact, new infected cases in Europe have risen sharply since autumn. On Oct. 14, daily new cases increased to 105,000 in Europe, outnumbering Asia's 103,000. On Oct. 15, new cases of infections in Germany soared to 6,638 in the past 24 hours, reaching a daily level not seen since the start of the pandemic.
Report 9received a chorus of criticism in the U.K., because people worried about the impact of lockdown restrictions on economy. The report predicted the novel coronavirus would kill 510,000 people in the U.K., if mitigation measures were not in place. As a result of measures like restrictions, deaths in the U.K. had been capped under 43,000 by Oct. 11. Despite obvious effect, U.K. lockdown rules were lifted when there were still cases for fear of an economic downturn. The "Coexisting with COVID-19 Policy" led to a surge in infections in the U.K. in autumn, prompting London to upgrade its COVID alert level from medium to high on Oct. 15.
By May 11, 31,000 deaths had been caused by COVID-19 in Italy. However, the country lifted the two-month lockdown in early May to reopen its economy. As Chart 2 shows, in the five months from May 11 to Oct. 11, death rates in Italy dropped from 14% to 4%, meaning that Italy had survived from its medical care system collapse. But the pandemic returned in autumn, after the country adopted the "Coexisting with COVID-19 Policy". On Oct. 14, the number of daily new cases climbed to 7,300, the highest since the start of the outbreak in March. In response, Italy had to once again ban dining together, and order restaurants to close before midnight.
On Oct. 25, Spain announced the state of emergency and implemented a curfew to rein in the second outbreak. On Oct. 29, Spain's parliament voted to keep the country's state of emergency in place until May 2021.
The outbreak also resurged in France. On Oct. 14, French President Emmanuel Macron announced the 9 p.m. to 6 a.m. curfew starting Oct. 17 in nine cities including Paris and Marseille. On Oct .15, French Prime Minister Jean Castex declared a national state of health emergency starting Oct. 17. On the same day, France reported the number of new daily infections jumped above 30,000, setting a one-day record. On Oct. 30, France began its second nationwide lockdown. On Nov. 6, France registered a record 60,000 plus new cases, triggering more stringent restrictions.
US President Donald Trump said long-term nationwide lockdown is not a solution. In late May, the Trump administration decided to restart economy in all states, regardless of the spreading virus. As case numbers rose sharply, New York had to announce a partial lockdown starting Oct. 4. From Nov. 4, daily new infection numbers in the US kept above 100,000 for many days in a row, repeatedly setting new highs. On Nov. 7, the tally of confirmed cases surpassed 10 million in the US, and total deaths reached 242,339.
Those European countries, the US and Japan, which adopted the "Coexisting with COVID-19 Policy", had to resort to lockdown measures to stop the spread of the virus.
- China achieves key results in 10-year fishing ban on Yangtze River
- Line 4 of Fuzhou Metro begins operation
- Taiwan people pick 'dismiss' as most representative word of 2025
- Competition to spotlight rescue robots, embodied intelligence
- Progress grows on seed vault project in Xiong'an
- 2 Chinese pioneers honored by Nature




































